Shackleton Fracture Zone

The Shackleton Fracture Zone (SFZ) is an undersea fracture zone, mid-oceanic ridge[1] and fault located in the Drake Passage, at the separation between the Scotia Plate from the Antarctic Plate.[2] It extends between 59° and 60°40' south latitude and between 56°30' and 61° west longitude and runs in a northwest to southeast direction from the South American continental shelf to the South Shetland Islands. Chile claims the area as part of its Outer Continental Shelf boundary.
The name, recognized by the Advisory Committee on Underwater Features (ACUF) since June 1987, is named after the British polar explorer Ernest Shackleton (1874-1922).
Natural delimitation between the Pacific and South Atlantic oceans
[edit]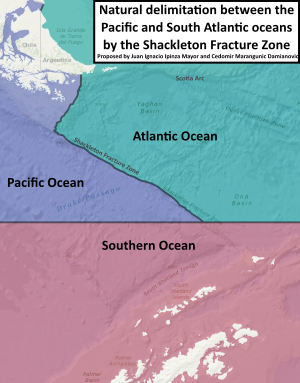
Scientists in Chile and other countries postulated that the boundary between the southeastern Pacific Ocean and the southwestern Atlantic Ocean was not the Cape Horn meridian, but rather the Shackleton Fracture Zone mid-oceanic ridge[1] and a submarine orographic chain which links the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago with the Antarctic continent. It also considers the conventional border of the Southern Ocean at the 60°S parallel.[3]
The researchers Juan Ignacio Ipinza Mayor and Cedomir Marangunic Damianovic put forward the scientific theory that the separation of the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean oceans "could be confirmed from the so-called Shackleton Fracture Zone (...) the boundary is then located east of the so-called Cape Horn Meridian".[4]
In 2019, the scientific journal Geology is News published "The SFZ separates tectonic plates and oceans, to the east the Scotia Plate and to the west the Antarctic Plate (which includes the former Phoenix Plate), and to the east the Pacific Ocean and to the west the Atlantic Ocean."[5]
In 2004 The Geological Society of America in the scientific paper entitled Shackleton Fracture Zone: No barrier to early circumpolar ocean circulation posits that: "the Shackleton Fracture Zone could have blocked the gateway until the early Miocene. Geophysical and geochemical evidence presented here suggests that the Shackleton Fracture Zone is an oceanic transverse ridge".[1]
See also
[edit]- Ernest Shackleton
- Borders of the oceans
- Natural delimitation between the Pacific and South Atlantic oceans by the Scotia Arc
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Roy Livermore; Graeme Eagles; Peter Morris; Andrés Maldonado (September 2004). "Shackleton Fracture Zone: No barrier to early circumpolar ocean circulation". Geology. 32 (9): 797. Bibcode:2004Geo....32..797L. doi:10.1130/G20537.1. hdl:10261/18847. ISSN 1553-040X.
- ^ "TECTÓNICA DE PLACAS Y CLIMA: la formación del Paso de Drake (Antártida)". La Geología es Noticia (in Spanish). March 27, 2019.
- ^ "There's a new ocean now-can you name all 5?". National Geographic. 8 June 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ Juan Ignacio Ipinza Mayor; Cedomir Marangunic Damianovic (2021). "ALGUNAS CONSECUENCIAS JURÍDICAS DE LA INVOCACIÓN POR PARTE DE CHILE DE LA "TEORÍA DE LA DELIMITACIÓN NATURAL DE LOS OCÉANOS" EN EL DIFERENDO SOBRE LA PLATAFORMA CONTINENTAL AUSTRAL". ANEPE (in Spanish).
- ^ "TECTÓNICA DE PLACAS Y CLIMA: la formación del Paso de Drake (Antártida)". La Geología es Noticia (in Spanish). March 27, 2019.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Shackleton Fracture Zone". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Shackleton Fracture Zone". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
60°0′S 60°0′W / 60.000°S 60.000°W
